All About Hearing Loss
How We Hear
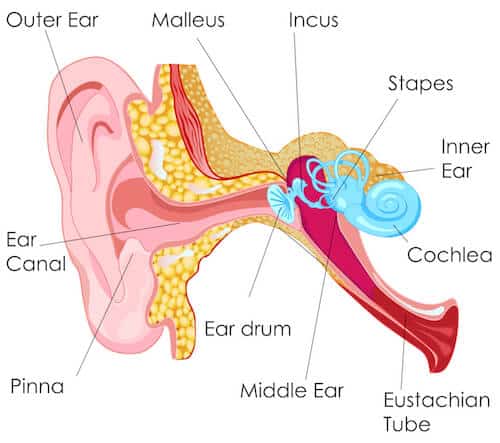
Many individuals often ask the question “What is hearing loss and how does it really affect me?” A person with hearing loss generally is able to hear some sounds very well while others seem muted, faint or not at all. 4 out of every 1,000 babies are born with hearing loss, making it one of the most common birth defects in the United States. To further understand what hearing loss is, it helps to understand how we hear. Sound waves entering the ear canal are directed to the eardrum, which conducts vibrations through the small bones of the middle ear to the cochlea. The cochlea is a snail shaped organ, known as the organ of hearing, and is lined with thousands of tiny little hair cells. Each hair cell or nerve ending responds to certain sound frequencies that send nerve impulses to the brain which are interpreted as sounds.
So your brain actually does the hearing, the ears are simply the mechanism to convert sound energy outside your head to nerve impulses your brain translates into sounds. Any sound impulse in your right ear is sent to the left side of your brain and any sound impulse in your left ear is sent to the right side of your brain.
Untreated Hearing Loss
If you or a loved one is suffering from untreated hearing loss there are some important facts you should know. Not being able to hear can have long term health consequences aside from creating the obvious communication problems. A number of studies have shown that not being able to hear is linked to brain atrophy in older adults which directly increases your risk of conditions like Alzheimer’s or Dementia. If you or someone you care about is suffering please take action today. The cannot afford to continue putting hearing loss on the back burner of your health care needs.

Untreated Hearing Loss Can Affect the Following:
- Intimacy and warmth in family relationships
- General communication
- Sense of control over your life
- Social participation
- Perception of mental functioning
- Emotional stability
- Communication in relationships
- Untreated hearing loss may increase your risk of Alzheimer’s. (Archives of Neurology Feb. 2012)
- Mild hearing loss linked to brain atrophy in older adults (Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania Aug. 2011)
- Hearing Loss is twice as common in adults with diabetes (Annals of Internal Medicine July 2008)
Types of Hearing Loss
A free diagnostic hearing examination from My Hearing Centers can determine what type of hearing loss you have and what steps are necessary to correct the problem. My Hearing Centers has locations in Arizona, Idaho, Nevada, Oregon, and Utah, California, and Wyoming. Please contact a location nearest you to learn more hearing loss and improving your hearing.
Age, noise exposure, disease, medication, trauma, and heredity or all common causes of hearing loss. Your hearing is a very complex sense and actually the most important one that you have. Most people would suggest their eyes to be the most important sense. But when you think about it, your eyes keep you in touch with objects or things. Your ears keep you in touch with people. There are three basic types of hearing loss:
Sensorineural
The most common type, it occurs when nerves in the cochlea are damaged and do not properly transmit auditory signals to the brain. This type is typically caused because of age or noise exposure and is very correctable with hearing instruments.
Conductive
Is typically the result of obstructions in the ear such as wax or physiological problems to the mechanics of the eardrum or small bones of the middle ear. In some cases these issues can be treated medically or surgically.
Mixed
A combination of sensorineural and conductive.
Interested in Hearing Better?
Schedule an appointment or call 1 (877) 330 2920.
Let us show you the difference My Hearing Centers can make!

